Advanced Concepts for Aero-Structures with Integrated Antennas and Sensors (ACASIAS). The European ACASIAS project will be reducing the energy consumption of aeroplanes in the future by improving their aerodynamic performance. NLR, together with Fokker Aerostructures, is investigating smarter ways of using parts of the fuselage by adding functions to them, such as building in a beamforming antenna.
The challenge
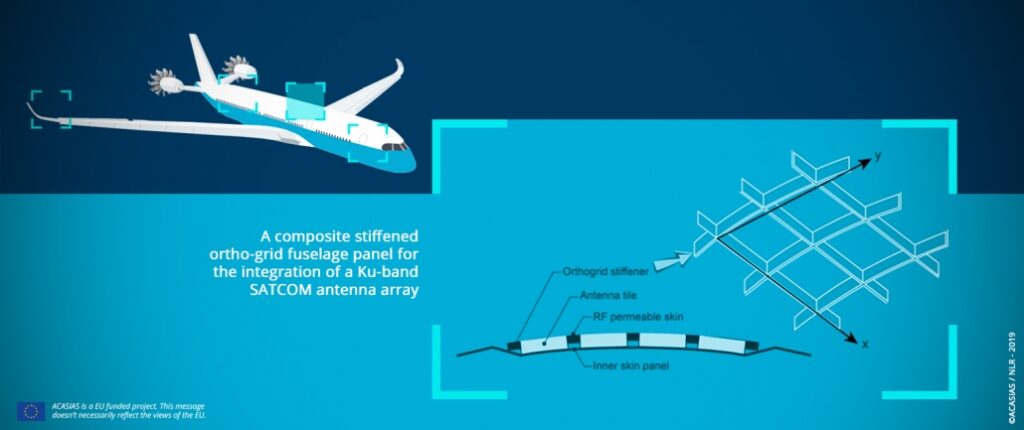
Aircraft drag reduction is an important issue for cleaner air transport. Up to now, satellite antennas are positioned on top of the aircraft in large protruding radomes. Within the ACASIAS project, Royal NLR is investigating the possibilities to integrate antennas in the structure to create smoother outer surfaces.
The solution
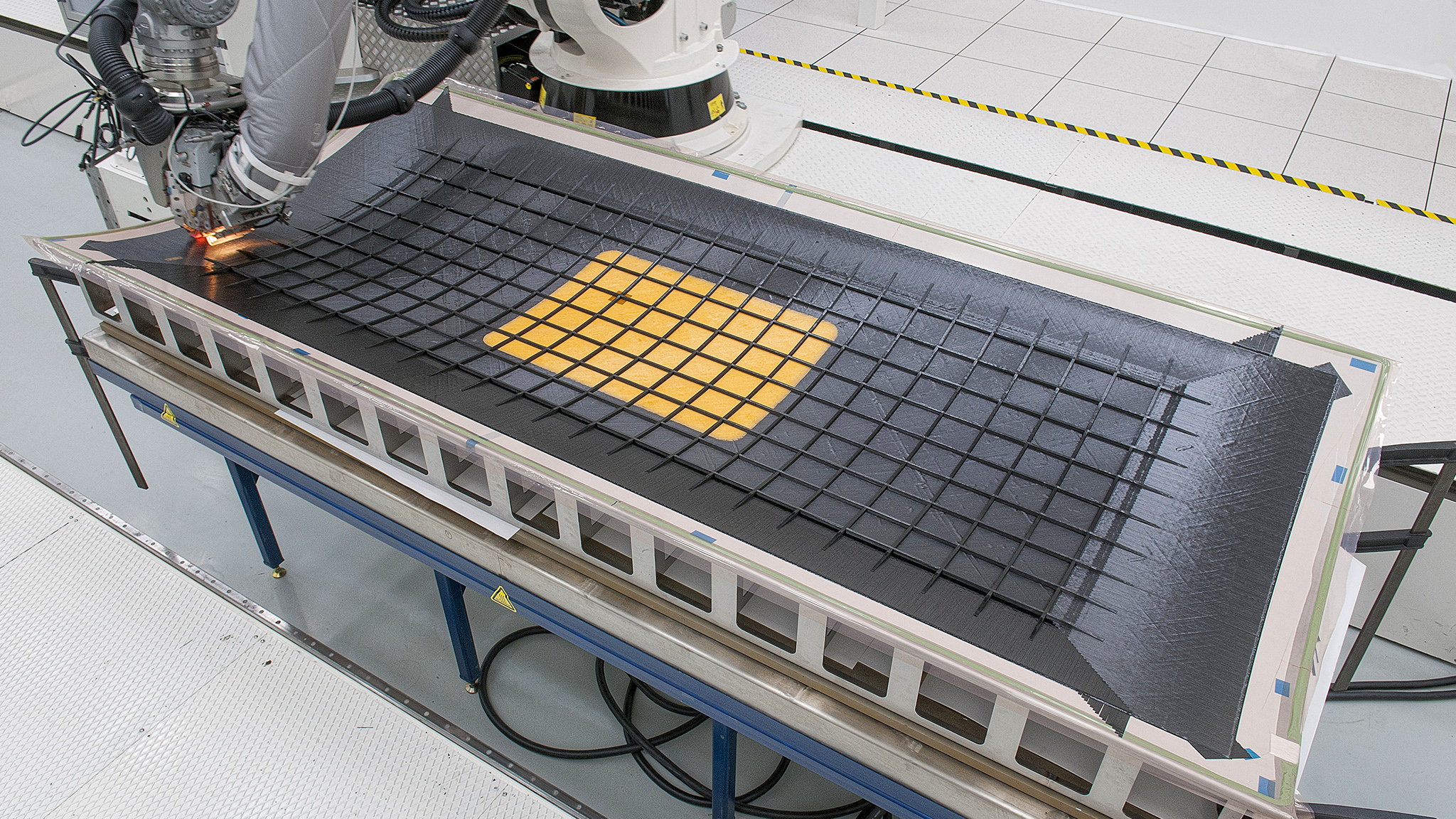
NLR and the ACASIAS partners have developed new beamforming Ku-band antennas, but also new composite structures with integrated antennas. The ACASIAS fuselage panel is made with a fibre placement machine, using carbon fibre prepreg. NLR has optimised the process for the manufacturing of thin stiffeners so no thickness build up occurs. In the middle of the panel, glass fibre prepreg is used to create a transparent skin for the internal antennas. By doing so, antennas can be placed on the inside instead of on the top of an aircraft, reducing the total drag of the aircraft.
What did we do?
NLR has optimised the process for the manufacturing of thin stiffeners. In the crossings of the lattice structure, half of the tapes are cut in one direction and half of the tapes are cut in the opposite direction, so no thickness build up occurs. In the middle of the panel, glass fibre prepreg is used to create a transparent skin for the internal antennas. The complete panel is cured on a female mould in an autoclave at a higher temperature and pressure.
To support the stiffeners during this process no labour intensive tools were used. Instead of the common used high number of supporting blocks a silicon bag is developed. The silicon bag has the same pattern as the final panel with stiffeners. In this way, an affordable panel was made with integrated stiffeners. No man-hours are required for cleaning of tool blocks, bonding of stiffeners or the installation of fasteners to connect stiffeners
Project partners:
Industry (NL) : Fokker Aerostructures
Industry (EU) : Diehl
Research organisations : NLR, (DLR, Fraunhofer)
Universities : Delft University of Technology (TUD)
Start : September 2017
Duration : 6 years

ACASIAS is funded by Horizon 2020. This message does not necessarily reflect the views of the EU.