Optimising the engine thrust frame of the Ariane 6 launcher. The Ariane 6 Launcher will enter a very competitive commercial launcher market. New entrants to this market have reduced the launch price per unit mass payload by half (50%). Compared to Ariane 5 the production costs of the Ariane 6 launcher should be reduced by at least 50%.
The challenge
A key requirement for the development of the Ariane 6 is reduced recurring production costs and increased performance. Cost reductions and performance increase (both stiffness and mass) is to be realised in proposed materials, manufacturing technologies, processes, procedures and optimisation of the industrial organisation.
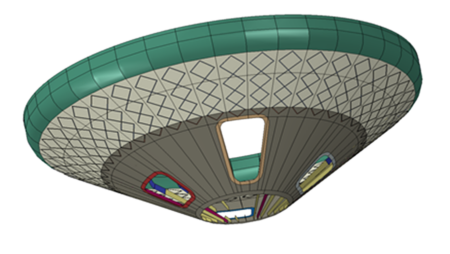
The solution
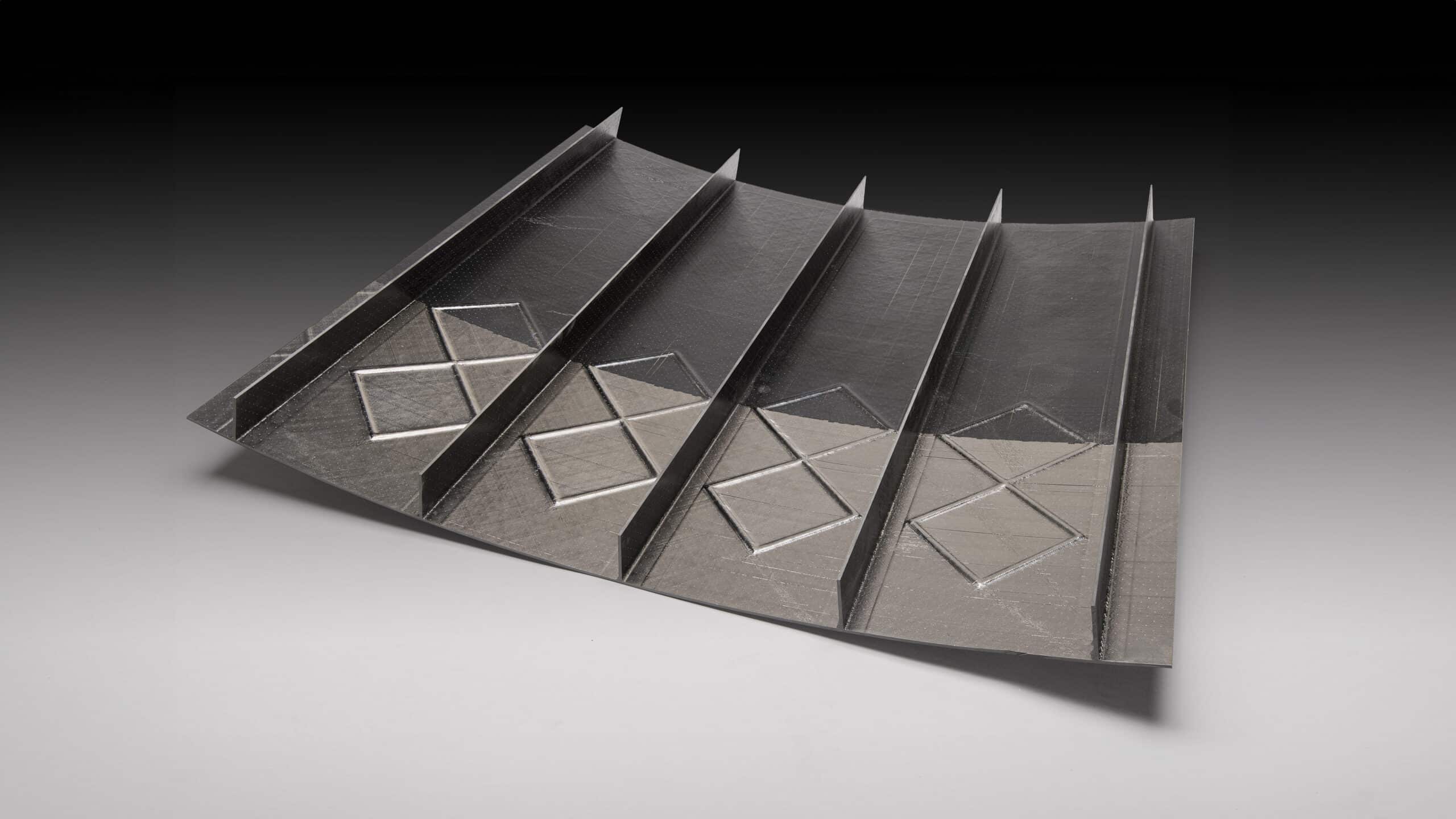
Currently, engine thrust frames for launchers are made from metal. Previous programs showed that cost and weight can significantly be reduced by application of carbon fibre reinforced polymers (CFRP) in tailored ply architectures, processed by the automated fibre placement technology. Based on a reference finite element model provided by Airbus DS NL, NLR developed optimisation to reduce the amount of manufacturing steps and tooling and to create vector fields for the steered plies. This innovative design in combination with the automated fibre placement technology will lower knock-down factors, reduce weight and minimize scrap material, resulting in reduction of material and energy consumption, processing time and increased payload.
What did we do?
NLR developed optimisation to reduce the amount of manufacturing steps and tooling and to create vector fields for the steered plies. Dedicated local reinforcements are composed by smart overlapping in order to improve the buckling behaviour between the reduced amount of blade stiffeners. This innovative optimisation method is combined with the automated fibre placement technology.
In addition, fibre detection methods are integrated by Infactory Solutions into the automated fibre placement technology. Possible material defects like gaps, overlaps or twists are detected, analysed and written to a database. Corrections are applied in order to support first time right production for further cost reductions.
Project partners:
Industry (NL) : European Space Agency – Future Launchers Preparatory Programme (FLPP)
Prime : Airbus Defence and Space Netherlands
Subs : Royal NLR, Infactory Solutions
Start : 2018
Duration : 2 years

This message does not necessarily reflect the views of ESA.




